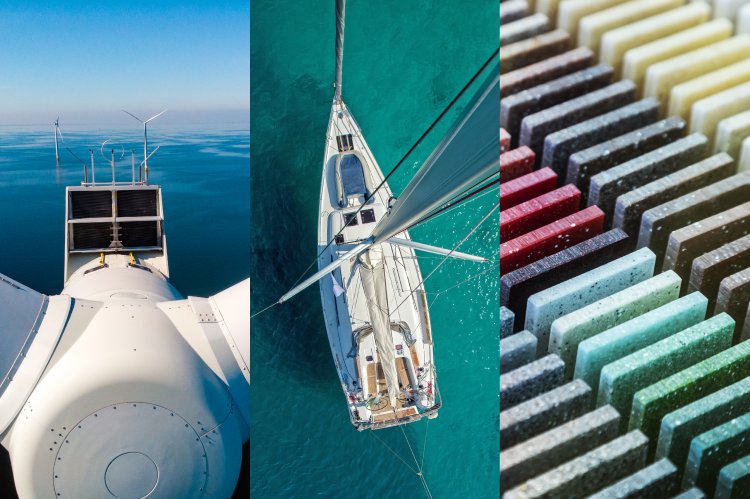
Unsaturated polyesters are synthetic copolymers with applications such as fibers, plastics, composites, and coatings. Depending on the choice of monomers, initiators, curing agents, additives, and modifiers used, various types of these products can be produced, exhibiting a wide range of chemical and mechanical properties. The cost-effective production of these products has made them highly attractive.
The primary use of unsaturated polyester resins is as a matrix in the composite industry. Based on their structure, unsaturated polyester resins can be classified into various types such as orthophthalic, isophthalic, pure maleic, and so on.
Ortho resins, or general-purpose polyester resins, are based on orthophthalic acid, meaning phthalic anhydride, maleic anhydride/fumaric acid, and glycols. Phthalic anhydride is relatively inexpensive and contributes to the structural strength of the final product. However, it has limited heat resistance, chemical resistance, and processability.
Among the glycols, resins synthesized with 2,1-propylene glycol are more important than products derived from other glycols. The methyl group present in 2,1-propylene glycol reduces the crystallinity of the resin and enhances its compatibility with common reactive solvents (such as styrene).
Iso resins are prepared using isophthalic acid, maleic anhydride/fumaric acid, and glycols. This category of unsaturated polyester resins is relatively expensive and has high viscosity. Therefore, a significant amount of reactive diluents (such as styrene) is used in their production, which improves their resistance to water and alkaline environments. Due to their heat resistance, chemical resistance, and better mechanical properties, these products find extensive use as coatings in marine environments.
Unsaturated polyesters are synthetic copolymers with applications such as fibers, plastics, composites, and coatings. Depending on the choice of monomers, initiators, curing agents, additives, and modifiers used, various types of these products can be produced, exhibiting a wide range of chemical and mechanical properties. The cost-effective production of these products has made them highly attractive.
The primary use of unsaturated polyester resins is as a matrix in the composite industry. Based on their structure, unsaturated polyester resins can be classified into various types such as orthophthalic, isophthalic, pure maleic, and so on.
Ortho resins, or general-purpose polyester resins, are based on orthophthalic acid, meaning phthalic anhydride, maleic anhydride/fumaric acid, and glycols. Phthalic anhydride is relatively inexpensive and contributes to the structural strength of the final product. However, it has limited heat resistance, chemical resistance, and processability.
Among the glycols, resins synthesized with 2,1-propylene glycol are more important than products derived from other glycols. The methyl group present in 2,1-propylene glycol reduces the crystallinity of the resin and enhances its compatibility with common reactive solvents (such as styrene).
Iso resins are prepared using isophthalic acid, maleic anhydride/fumaric acid, and glycols. This category of unsaturated polyester resins is relatively expensive and has high viscosity. Therefore, a significant amount of reactive diluents (such as styrene) is used in their production, which improves their resistance to water and alkaline environments. Due to their heat resistance, chemical resistance, and better mechanical properties, these products find extensive use as coatings in marine environments.